Introduction
Registering a company in China offers a significant opportunity to gain admission toward the Asian trade and solutions as a platform for worldwide speculation plus growth. The Republic of China also known as China is a major player in the worldwide economic scene, with a GDP of approximately $14 trillion. The nation enjoys leading positions in numerous industries, including production, innovation, venture, and infrastructure, and its fiscal sector is expanding at a steady rate.
Due to its diverse fiscal sector, access to affordable labor, and strong center on creativity and modernization, the Republic of China presents substantial possibilities for attracting FDI. The completion of the Foreign Investment Law has established everything fair, warranting non-occupants to oversee operations under conditions like those for homegrown venture visionaries. The merits of implementing commercial endeavours in the Chinese mainland are emphasised by this change.
This distribution will frame prerequisites for establishing a Chinese endeavour, investigate the various sorts of legitimate corporations accessible for alien fiscal backers, and feature promotional schemes for trade visionaries planning develop an operation in the People's Republic of China
Pros of forming an organisation in China in 2026.
Entities searching for global growth have long chosen the way towards opening a company in China . The Republic of China is well-acquainted for the many economic prospects it offers. Presented right below are the principal Impact of opening a Company in the PRC:
- The worthwhile topographical field in the Far East gives chances to obtain adjoining markets.
- Chance to reap rewards via among the biggest consumers in the globe's monetary spheres, exceeding 1.4 billion individuals and is growing.
- Created transport and coordinated factors framework, close by admittance to particular work force.
- The Republic of China's expanding economy is largely driven by technological innovation, which streamlines business sequences.
- Charge impetuses and duty decreases for imported hardware, joined with the accessibility of moderately reasonable gear plus unrefined materials, aid with bringing down working expenses.
- Capacity to open a company in China without a visit without the prerequisite for an actual visit.
- Driving the economy with regards to purchasing power parity (PPP) because of fast fiscal development.
- Work costs remain nearly low.
- An amazing possibility arises with the improvement of western territories, especially Sichuan.
In the event of establishing a firm in China, the Foreign Investment Law, which went into force in January 2020, is the vital important regulation to examine. The legislation fosters equitable competition, combats corruption, standardised foreign investment supervisors, and strengthens rights for foreign shareholders and their Chinese capital expenditures.
- Motivated sectors include consultation, manufacturing, and commerce.
- Restricted Corporations involve networking and mineral exploitation.
- Prohibited Operations include transportation within the territory.
The China International Investment Promotion Agency sets up the spread of intelligence about the permissions needed to initiate a venture in PRC. All planned foreign investment undertakings shall go through a "survey" by the NDRC or the relevant commonplace/nearby compensation, taking into account the geography and the worth of the enterprise.
When an international investor is involved in opening a 100% foreign-owned enterprise (WFOE) in the Republic of China, they have full strategic directive throughout the duration of the undertaking schemes and earnings. The registration of a WFOE in China shows that a nation’s financier's direct involvement is unnecessary. Since there isn't a motivating factor to disclose corporation information with an associate within the nation, a WFOE is an imperative alternative for protecting your IP in China. Nonetheless, maintain consideration that the enrollment sequence is supervised by several municipal ordinances and rules.
A WFOE can hire both indigenous and overseas labor, offering flexible choices that lessen the necessity for Chinese collaborators. As a result, transnational stockholders searching to join Asian markets usually apply the WFOE. Importantly, opening a WFOE in China does not necessitate a specific minimum starting capitalization.
Furthermore, enrolling a venture with 100% non-domestic management in China as a trading WFOE can be successful, permitting international organisations to send and receive goods, established brands, trade commodities, and open online commercial storefronts. Such firms provide solutions for storage, warehousing, management of inventory, delivery of services, and servicing.
International stockholders may establish 100% foreign-owned firms in the Republic of China by forming consulting or creating WFOE. Each of these sorts needs a warrant appropriate to its specified operations.
Registration of a representative office in China
The regional office has no authority to perform trading for the intended reason of making a profit. But it could function for marketing research, studying competitors; can become the basis for scientific research in various fields (including cooperation with universities, scientific institutes alongside further endeavors); for other non-profitable operations. Organising conferences, seminars and venture meetings can become A vital component of the branch's operations, encouraging trading of expertise plus expansion of the firm relations of an alien organisation.
Registration of a joint venture in China
This covers a joint effort arrangement in which a Chinese affiliate holds an ownership rate of exceeding half. A joint venture provides a significant value of providing foreign investors with access to limited industries such as training, communications, healthcare facilities, oil and gas extraction, as well as others that they may not possess capacity to obtain through other administrative and judicial sequences. This is addressed with the inclusion of an adjacent affiliate in the endeavour's arrangement. Another significant advantage is the lack of basic expenditure requirements, which makes this system alluring to aspiring entrepreneurial visionaries and sole proprietors. The following section provides an assessment of the already mentioned entities.
Registration of a branch in China
Major worldwide partnerships have the choice to lead tasks in the Republic of China by laying out branches. Using branches to oversee exercises in international nations, like China, is generally taken on training. This empowers foreign organisations to use the merits of their own authoritative design and guidelines while complying with nearby legitimate commitments and conditions.
Subsidiaries typically adhere to the plans and techniques established by the alien organization, ensuring uniformity in company operations and executives. However, corporations are also required to adhere to the host nation's legitimate criteria in order to avoid conflicts with local directives and ensure the legality of their actions.
Managing branches may pose extra risks and complexities as a result of differences in law, costs, and strategic decisions. As a result, while considering opening a branch in China , It is vital to attract specific legal counsel. Their skills can greatly ease out the enrolling process and reduce any difficulties.
|
OPF |
Merits |
Peculiarities |
|
Opening of WFOE in China |
|
There are no criteria for authorized fund (unless particular fields are utilized into account, and the requisite stake is decided at a certain amount). |
|
Opening a representative office in China |
|
|
|
Opening a joint venture in China |
|
Profits are divided between partners. |
|
Opening a Branch in China |
|
|
Starting a company in China demands an extensive knowledge under the fundamentals of officially authorised stock and directives that govern your venture. Inputs to the funds are excluded from levying charges and can be collected and compensated in cash, innovation, equipment, or other holdings.
The predefined acceptable stock will be identified in the AoA. Previously, Foreign-invested enterprises (FIEs) were needed to meet strong basic funding standards. Nonetheless, in 2014, alters to the Companies Law eliminated the set minimum capital requirement for Wholly Foreign-Owned Firms. Designating a significant quantity of money, often enough to cover expenditures for at least between six and twelve months, is crucial.
Features and prerequisites for forming an entity in China.
To take full leverage of the numerous leverages that are available in this nation's financial sector, it must conform with the correct steps to register a company within the jurisdiction in line with the statutes that apply.
Principal sequence of organisation enrollment in China :
- Specify the company's form.
- Enrol to secure your initial moniker.
- Assemble a collection of enrollment paperwork.
- Pay the fees.
- Hand over the indenture and mandatory documentation to the proper regulator for evaluation.
For parties seeking to conduct venture in China, market study is a must.
- Shanghai: Recognized as an transnational port and the nation's city with the highest GDP, Shanghai has long positioned itself as a major entry point for foreign financiers accessing the Chinese market. Forbes has repeatedly placed Shanghai as the best Chinese city for commerce, due in enormous measure to the city's vibrant and clear regulatory system, which draws global speculation.
- Beijing: As the largest city, Beijing quickly became one among the globe's leading trading hubs. It serves as both the nation's political epicentre and a center for science, education, and art.
- Shenzhen and the Greater Bay Area: Shenzhen is known throughout the Asian territory as a hotbed for initiating technological ventures. Notable enterprises such as Tencent, DJI, Huawei, and BYD have launched profitable ventures across the city.
The underlying stage lays out the planning for grasping the area, pinpointing venture possibilities, and hence recognizing objective customer base. Additionally, it makes it simpler to evaluate readily available resources and anticipate potential dangers.
Utilizing organisation naming terms associated with particular industries or of societal and pecuniary significance in enterprise titles necessitates regulatory endorsements in attempt to gain permission for the corporate moniker. Instances of such terms envelop "Bank" or "Insurance" and other associated articulations.
Following this, one needs to embrace some methods to obtain a licence to do business in China. You are additionally needed for enrollment with the Tax Management and opening an account in a Chinese bank. All legislative entities are expected to enrol with the Business Agency, which awards permissions and manages their schemes.
To acquire a certificate, an application should be conveyed to two particular authoritative bodies: the Ministry of Commerce and the State Administration for Industry and Commerce. These organisations regulate commercial operations in China, assuring adherence to pertinent guidelines. Giving exhaustive files is urgent to the fruitful finish of these systems.
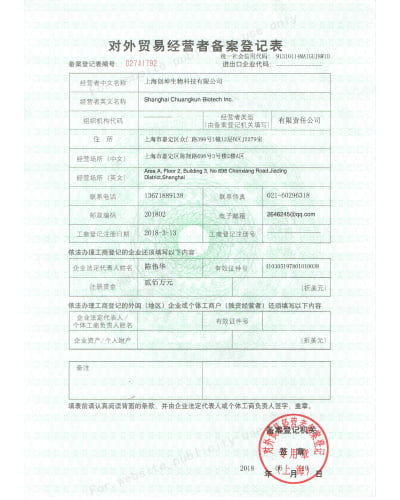
Caption for illustration: business registration in China Application form.
To sign up an enterprise in China, you should compile an outstanding collection of paperwork:
- Official trade name certification
- Verified office location
- Identification subtleties of the legislative representative and firm supervisor
- Shareholder and director particulars
- Notarized shareholder documents
- AoA and MoA
- Registered capital details
- Pecuniary feasibility analysis and bill
- List of governing associates
- Organisational model and administrative setup
A feasibility report, which comprises a functioning program and finances, mandates to be created before registering a company in China to show the directors that the organisation is viable. The firm's strategic plan ought to incorporate goals, approaches, market studies, advertising tactics, operational plans, and projected revenues. The budget should include a detailed breakdown of expected income and expenditures for a specific time period. It is critical for companies to provide detailed rationales and justifications for all financial transactions in order for experts to thoroughly examine their financial condition. The typical application cycle lasts between 12 and 26 weeks.
Opening a company in the SEZ of China
The control established SEZs to promote commerce and monetary growth. Unlike the mainland, SEZs provide entrepreneurs with flexible policies for running a corporation, notably streamlined customs clearance processes. These zones also authorise permission to sophisticated communication organisations.
The positive effects and benefits provided by these regions enable the successful optimisation of manufacture and operational processes, cost reduction, and benefit growth. Furthermore, the FTZ diverse infrastructure, which includes sophisticated facilities and centers of transportation, lays a firm foundation for the firm’s performance.
Registration of a company in Chinese FTZs delivers a quantity of privileges and merits:
- Levy breaks for commercial enterprises.
- Simplified customs procedures.
- Simplification of monetary administration.
- Availability of financial help.
- Industrial corporate administrations.
|
SEZ of China |
|||
|
Shanghai FTZ |
Fujian FTZ |
Guangdong FTZ |
Tianjin FTZ |
|
This FTZ got created in 2013 with the aim of attracting firms specializing in the following sectors:
|
This zone was created in 2014. This area is focused on a number of strategically important areas, including advanced manufacturing, tourism, the development of maritime transport routes, and innovation present in the world of finance. |
This FTA was launched in Guangdong in 2015 to strengthen mainland China's ties with Macau and Hong Kong. This initiative aims to advance maritime trade routes, especially towards Europe and Africa, and has the strategic objective of becoming a financial center, industrial hub, and global leader in shipping and logistics. |
This FTZ was launched in 2015. This innovative economic region emphasises on establishing groundbreaking technology.. production, fiscal leasing, and cross-border logistics routes. The purpose of launching this zone is to set up a major platform for stabilising Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei trade relations. |
Registration of a company in China by non-resident in specialised high-tech parks is also possible, often known as technological zones. These areas are distinguished by their concentration on technical firms or regions, which deal with resource gathering in certain places and developing their turn of events.
Officials provide a variety of incentives for entrepreneurs and visionaries interested in opening a company in a high-tech zone in China, including tax breaks, sponsorships, and support. Furthermore, these regions have modern infrastructure, including office and production areas, incubation facilities, and other amenities, to assist firms that work within them.
Registration or purchase of a company in China : prospects for foreign venture
As previously mentioned, numerous overseas investors are expressing strong interest in building an endeavour in PRC In recent years, eight Chinese provinces have emerged as very appealing speculation locations, acting as hubs for global corporate ventures.
China offers many venture opportunities, several industries that are currently thriving:
- Tourism
- Education
- Monetary assistance
- Agriculture
- Food sector
- Infrastructure development
- Judicial assistance
- Information and networking technologies.
To guarantee that your organisation runs effectively, hire skilled specialists. They can offer ample details on the regulation of investment activities in China and support in registering a company in China at every level of the company application process.
Taxes and accounting in China
The typical charge is 25%, yet there are decreases accessible. Startups get a percentage of 20%, while high-tech ventures receive a rate of 15%. In particular, revenue up to three million yuan is assessed levy at ten percent,, while the revenues up to one million yuan are bound to levy at 5%.
- 13% for the supply of leasing solutions for tangible and movable assets, as well as for the import and sale of general goods.
- 9 percent for the transportation, basic telecommunications, and building service, as well as the sale and import of specific goods.
- 6% for the sale of intangible assets, monetary services, and additional telecommunications, excluding land use rights.
Accounting services in China have specific features. The country uses its own fiscal and reporting system that is distinct from Western standards. The China Accounting Standard (CAS) came into effect in 2007, plus it is closely compatible along with the International Financial Reporting Standards. However, there remains variations in implementation and comprehension.
The CAS arrangement is built on two major regulations:
- Accounting Standards for Business Enterprises (ASBE): These principles govern the bookkeeping cycles and procedures of big and medium-sized businesses.
- Accounting Standards for Small Businesses (ASSBE): These concepts are tailored for small ventures.
To operate efficiently in the Asian country, firms must adhere to pecuniary detailing and disclosure standards. Enterprises are normally obliged to file yearly accounting records, which include a balance sheet, earnings statement, cash flow statement, and references to the bookkeeping reports.
Furthermore, enterprises in China must meet stringent disclosure requirements to ensure transparency for collaborators and supervisors. This includes relevant financial information such as revenue, expenditure, resources, liabilities, and contingent obligations. To avoid penalties or legal ramifications, disclosure reports and financial statements must be filed by certain timeframes.
|
Business establishment in China : levy incentives |
||
|
Industry CIT Incentives |
CIT benefits (15% reduced rate) based on location |
Levy benefits depending on venture size |
|
As part of China's drive to boost its technological capabilities and move towards digitalization, significant tax incentives are available. For example, from 1 January 2020, key software and IP businesses benefited from a reduced 10% CIT rate.
Approved new/high-tech firms and qualifying SMEs participating in pollution prevention control, you may additionally take advantage of a fifteen percent CIT charge reduction (valid for the latter until December 31, 2027).
Enterprises in the farming technology sector are completely spared from revenue taxes.. |
This applies to enterprises founded in nations with limited resources in SEZs. Eg: Organisations working in one of the favoured sectors and located in the western region of the country (the benefit is valid until December 31, 2030); Companies involved within manufacturing and R&D in the Lingang area of the Shanghai pilot free trade zone (the benefit is valid for the first 5 years of their activity).
The same applies to firms in Shenzhen-Hong Kong Qianhai Zone who are qualified for the incentive. |
In this context, tax breaks are typically provided to startups and scant profit businesses with yearly revenues of up to three million yuan and fewer than 300 workers.
The jurisdiction authority government views small trade as the engine of the country's further pecuniary growth.This presents that China wants to make it easier for small trades to do trading there. It also wants to make it easier for new investors to start a business in the nation and get a foothold in their markets.
Among of the various levy breaks available to startups in the Republic of China are listed below: CIT incentives. Minor companies face a feasible CIT rate that exceeds 5%, irrespective of sector or region. The beneficial effect will remain active until the end of the year in 2024. VAT benefits. Minor taxpayers subject to a 3% VAT rate may gain from a 1% VAT rate reduction. This merit will remain active until the last day of December 2027. |
Opening an account for a company in China
Opening a bank account for a company in China can be a difficult cycle, as various different cities and banks have their own particular prerequisites. Banks and controllers authorise strict rules for opening accounts for foreign companies to forestall tax evasion and other criminal operations.
In order to assess the risk of insolvency, fraudulent transactions, or other potential issues, banks may request a significant quantity of indentures and conduct additional checks.
List of mandatory documentation that must be provided in order to open an account for a Chinese company :
- Evidence of establishment, such as a present company permit, a Tax Service authorization licence, or the company's AoA.
- A comprehensive identification file for the corporation's authorised representatives.
- A clear representation of the organisational framework.
Notable financial institutions in PRC
- DBS Mainland NRA Branch
- ICBC
- HSBC Mainland NRA Branch
- Bank of China Ltd
- Agricultural Bank of China
- China Construction Bank
- China Merchants Bank
- OCBC Wing Hang Bank China
The RMB basic fund is utilised in enterprises with international speculations everyday expenditures in the Republic of China. This account allows you to withdraw RMB cash and is frequently utilised to compensate for levies. To gain funding from overseas, you must have a transnational stock account. The State Administration of Foreign Exchange (SAFE) must authorize the initiation of this account.
Liquidation of a company in China
A complicated deregistration procedure is needed when a Foreign-Invested Enterprise decides to stop functioning in the Republic of China. Failure to properly deregister a business in China can have serious legal repercussions. This interaction requires fastidious preparation and explicit advances.
To begin, the intention to cease operations must be communicated to all relevant government authorities. This incorporates nearby specialists, charge specialists, banks, and other administrative bodies. After that, the company needs to divide up its assets and pay its debts to suppliers and creditors.
It is critical to consent to nearby regulations in regards to the de-registration process. Meeting explicit circumstances or giving specific records before the enrollment can be for all time dropped is fundamental. This might include covering extraordinary charges, resolving legitimate discord, or getting exceptional authorization from local specialists.
The sequence to liquidate a company in China are as follows:
- Establishing a liquidation commission within 15 days of the liquidation decision.
- Submit a request to liquidate to the Ministry of Commerce (MOFCOM).
- Announcing the liquidation in a newspaper within 60 days of the commission's creation.
- The Tax Bureau approves of the liquidation.
- Assets are liquidated.
- The revocation of permits.
- Cancellation with other government officials, such as the Bureau of Social Security, the SAFE, and the Customs Administration.
- Terminating financial accounts.
Overall, if you are considering closing a company in China, you need to use experts to conduct the procedure. This maintains the authenticity of organisation affairs and improves the business's status as a credible market participant.
Summary
The jurisdiction is building its position as a prominent actor in global finance and financial markets, ranking among the globe's rapid-developing nations. The Asian nation has grown dramatically over the past several decades, transitioning from an economy centred on manufacturing to one of the globe's foremost buyers and sellers.
Regarding the numerous facets of starting a company in China is critical prior to founding a corporation in the Republic of China. The major significant corporate form is the Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprise, which permits a foreign national to possess the whole firm's assets. The People's Republic of China has implemented some efforts to enhance quality commercial settings for international firms, including functioning on cross-border intelligence streams and relaxing guidelines for granting business-related visas upon presentation. In addition, remote registration of a company in China is permitted.
We give support during the process of registering a company in China. Feel free to get in touch with us directly if you require additional intelligence on advice on regulating business activities in China.









 Audit and Accounting support
Audit and Accounting support China: registering a company and opening an account
China: registering a company and opening an account  How to open a corporate account in China
How to open a corporate account in China  Relocating business to China: Registering a company in the PRC
Relocating business to China: Registering a company in the PRC  Establishing a WFOE in China
Establishing a WFOE in China  China's Banking System: Characteristics and Integration Procedures
China's Banking System: Characteristics and Integration Procedures  Investment facilitation in China: navigating legal and business landscape
Investment facilitation in China: navigating legal and business landscape  Regulation of IPOs in China
Regulation of IPOs in China 



