Obtaining a crypto license in Indonesia is a legally significant step aimed at ensuring the legitimacy of licensees’ operations in one of the most promising digital asset markets in the Southeast Asia region. The Indonesian state, seeking to strengthen its position as a regional center of innovation, creates preferential conditions for the implementation of projects related to financial technologies, attracting investment and promoting the development of modern financial infrastructure.
Due to increasing interest in cryptocurrency transactions from both foreign and local entrepreneurs, obtaining a license for a cryptocurrency company in Indonesia acquires particular relevance, since it creates not only conditions for legitimate activities, but also for protecting the interests of all participants in the process. At the same time, the question remains open for new market participants about developing an effective strategy for entering the Indonesian cryptocurrency market while complying with all regulatory requirements established by the regulator.
The treatise expounds upon pivotal juridical facets and phases of procuring a cryptocurrency concession in Indonesia, matters pertaining to the amassment and formulation of requisite documentation, and the traverse of the authentication protocol for adherence to stipulated prerequisites are deliberated.
Obtaining a cryptocurrency license in Indonesia: factors of country attractiveness
The rapid growth of digital assets, which has led to a fundamental transformation of the global financial system, reached scales previously considered unattainable, with a total capitalization exceeding US$3 trillion. Indonesia is actively integrating into this innovative segment, demonstrating its commitment to financial modernization.
A propitious juridical framework and a steadfast macroeconomic milieu have engendered augmented intrigue among outlanders in procuring a cryptographic licensure in Indonesia. An escalating multitude of enterprises and personages are availing themselves of digital pecuniary instruments as a modality of remittance and capital allocation. The Indonesian crypto-monetary bazaar encompassed 28.65 million utilizers.
For the propitious actualization of pecuniary undertakings within the cryptosphere, adherence to all stipulations enshrined in jurisprudence and the procurement of licensure for crypto pecuniary operations in Indonesia are paramount, facilitating the attenuation of juridical perils and fostering unwavering mercantile proliferation. To engender a pellucid milieu conducive to the maturation of the crypto pecuniary domain, the Indonesian gubernatorial arbiter is effectuating a constellation of stratagems to legitimize and institutionalize its framework. Notably, nascent licensure paradigms for mercantile constituents are being architected and effectuated, gubernatorial adjudication modalities are undergoing refinement, and the echelon of onus incumbent upon digital asset facilitation entities is ascending.
Modifications to statutes inaugurated in 2024 concerning the protocol for the licensure of cryptographic pecuniary enterprises in Indonesia evince the nation's inclination toward meticulous codification of this sphere of the fiscal marketplace. The culminating juncture of these metamorphoses was the transference of prerogatives in the domain overseeing the governance of digital holdings in Indonesia by apportioning a fraction of the jurisdiction from the Commodity Futures Trading Supervisory Board to the Financial Services Authority (FSA). These juridical novelties necessitate the recalibration of mercantile frameworks of sectoral constituents to novel, more exacting stipulations, which, in turn, will fortify the pecuniary paradigm within the cryptographic domain and augment the quotient of credence among both indigenous and extraneous capitalists.
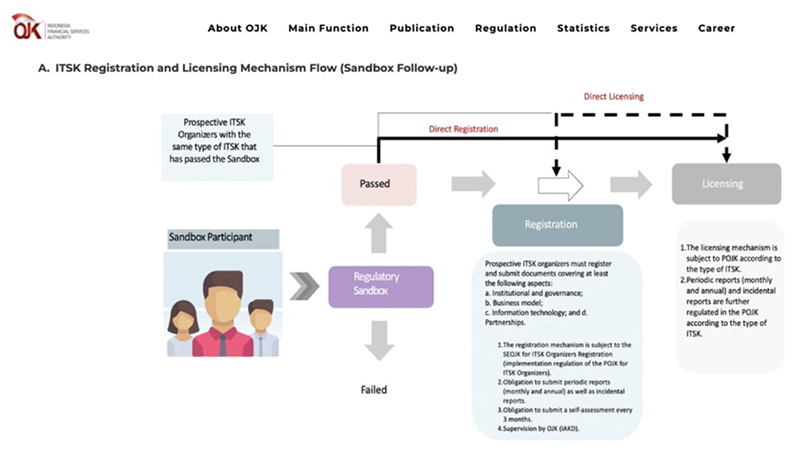
Illustration caption: Licensing of digital financial asset and crypto asset providers FSA.
Securing a cryptocurrency authorization in Indonesia is pivotal for enterprises to fortify their market stature. It substantiates adherence to organizational management norms and fiscal transparency, while permitting engagement with global affiliates and financiers. This credential facilitates involvement in substantial investment endeavors within both domestic and international arenas.
Indonesia functions as a transcontinental nexus for commercial evolution in the Orient and Southeastern Asia, presenting a malleable legislative framework for avant-garde fiscal tools such as cryptocurrencies. Its dynamic incorporation into global mercantile alliances propels the universalization of entrepreneurial paradigms.
Securing a patent for cryptocurrency asset undertakings in Indonesia grants enterprises the privilege to wholly engage in indigenous commerce, especially for individual investors in the Oriental expanse. This holds particular worth owing to the profound involvement of the youthful demographic.
Cryptocurrency regulation in Indonesia
Pursuant to the divulgation of the supervisory entity that administers the derivatives bazaar, concomitant with bourse mercantilism metrics, an unwavering ascendant proclivity is discernible in the quantum of dealings with cryptographic pecuniary instruments, signifying an amplification in predilection for numismatic digitization and its amalgamation into fiduciary circulations. These arithmetical expositions substantiate the prodigious propensities of the Indonesian emporium for the proliferation of undertakings in the crypto-economic sphere and evince the existence of a consequential cohort of pecuniary patrons predisposed to liaise with avant-garde fiscal contrivances.
Procuring a dispensation for dealings with cryptographic holdings in Indonesia endows commercial establishments with lawful prerogatives for assimilation into the indigenous pecuniary framework, affording ingress to an extensive gamut of fiscal contrivances. Nevertheless, antecedent to acquiring a cryptographic licensure in Indonesia, it remains imperative to acquaint oneself with every facet of the juridical governance extant for this mercantile subdivision.
The rudimentary ordinance overseeing the perambulation of cryptographic chattels is the Prospective Bartering Statute No. 32 of 1997, initially envisaged to administer contingent pecuniary apparatuses. In correlation with the mercurial augmentation of the fiscal bazaar and the advent of groundbreaking fiduciary implements, the lawgiver has unwaveringly refined this decree, attuning it to the idiosyncrasies of the vicissitude of ethereal denominations.
Amidst the gestation of the juridical scaffold in the realm of numinous holdings, the cryptographic licensure in Indonesia has garnered the stature of a paramount instrument contrived to ascertain efficacious pecuniary scrutiny, attenuate the perils of peculative purification, and vouchsafe limpidness and foreordainment of mercantile intercourse. The vicissitudes of the evolution of algorithmic tender have necessitated the incessant refinement of the regulative corpus. Statutory codices delineating the perambulation of electronic lucre and cryptographic specie have undergone cyclical reappraisal to accommodate emergent technocratic verities and supranational tenets.
The Indonesian juridical schema for cryptocurrency trading platforms is devised to advocate lawful marketplace undertakings, bolster societal scrutiny, and harmonize national statutes with international anti-money laundering doctrines, endeavoring to cultivate pecuniary progression whilst preserving financial equilibrium.
To acquire a cryptocurrency patent in Indonesia, enterprises must comply with juridical precepts, encompassing the register of digital commodities, dossier prerequisites, and permit solicitation terminuses. Conformance to anti-pecuniary laundering statutes is pivotal, as is ensuring clientele recognition and verification (KYC). Noncompliance may culminate in juridical repercussions, such as the repudiation of accreditation or curtailing the corporation's legitimate endeavors.
On January 12, 2025, Indonesia promulgated the Financial Omnibus Statute No. 4 [2023], metamorphosing the administration of the cryptographic sphere. This edict bestows upon the FSA augmented prerogatives, hitherto bestowed upon Bappebti, to supervise the monetary domain efficaciously. The objective is to forge a harmonious juridical schema, alleviate regulatory encumbrance upon market agents, and enhance fiscal concords.
The transfer of dominion is accompanied by a profound metamorphosis of the juridical condition of cryptocurrencies in Indonesia (which ranked third in the world according to the Chainalysis Cryptocurrency Adoption Index 2024), which shall inexorably influence all facets of the operation of the cryptographic sector, encompassing the legal condition of market denizens, the protocol for dealings with digital commodities, and the apparatus safeguarding of investors' entitlements.
Main characteristics of the new regulation of cryptocurrency activities in Indonesia:
- The regulatory body FSA has promulgated a Crypto Asset Compendium, delineating measures to integrate cryptographic commodities into the nation’s fiscal infrastructure. In the course of execution, it is envisioned to forge collaborations with credit establishments and ancillary financial entities, enunciate explicit stipulations for the realization of undertakings pertaining to the circulation of virtual assets, and furthermore guarantee that the populace is enlightened regarding the juridical status and prospects for the evolution of cryptocurrencies.
- To prime itself for the oversight of digital fiscal and crypto assets, FSA has instigated ventures such as interlocutor dialogues, internal fortification of capacities, and the establishment of a task force to address crypto sector predicaments.
- Formulation of a meticulous regulatory scaffold for all participants within the cryptocurrency domain, encompassing exchanges, crypto wallet purveyors, and other service purveyors. This architecture aspires to refine operations.
- FSA intends to effectuate a real-time reportage mechanism to surveil crypto transactions. This will substantially amplify the degree of translucency and responsibility within the digital asset marketplace, bestowing regulators with the acumen to expeditiously analyze pecuniary flows and unearth stratagems aimed at tax avoidance and money laundering.
To guarantee a concord between ingenuity and fiscal stability, FSA has instituted a regulated testbed paradigm, affording financial market participants the prospect to trial avant-garde fiscal commodities and services, encompassing solutions grounded in blockchain technology, within a supervised milieu. This enterprise substantiates Indonesia's tactical emphasis on fostering a conducive ecosystem for the advancement of financial technology.
Indonesia's cryptographic accreditation shall be pivotal in validating and systematizing virtual coin enterprises, safeguarding equitable rivalry. The licensure and supervision procedures for cryptocurrency platform administrators will be expounded, encompassing intricate stipulations, augmented baseline capital, and abbreviated durations for regulatory application resolutions. By the year's conclusion, a holistic governance scaffold will be instituted, assuring unambiguous technical parameters and foreseeable juridical directive fulfillment.
Please note here that Indonesia, seeking to strengthen its international authority and reputation as a reliable partner on the global stage, is actively integrating into international schemes for regulation of the cryptocurrency market. As a member of the G20, the country participates in multilateral dialogues aimed at harmonizing national approaches to combating money laundering in the context of the evolving digital environment.
Indonesian lawmakers are augmenting fiscal market oversight and cultivating a propitious regulatory milieu for blockchain technology ingenuity. They are investigating the deployment of cryptocurrency in commerce, logistics, and state procurement, guaranteeing transnational benchmarks and nurturing a novel echelon of digital economy advancement in the nation.
Contact our specialists
Who can get a crypto license in Indonesia?
An analysis of foreign experience shows that the crypto-asset market attracts a wide range of participants, including both technology startups and large corporate structures. To understand which legal entities can obtain a digital asset license in Indonesia, it is necessary to analyze the requirements for applicants. Current legislation establishes fairly strict selection criteria that must be met by entities wishing to legally operate in this market.
Cryptocurrency ventures in Indonesia necessitate meticulous deliberation of institutional and juridical entity stipulations. The predominant structure for inaugurating a cryptocurrency enterprise is a PT PMA, though Indonesian corporate legislation sanctions alternative organizational configurations, contingent upon prescribed doctrines.
The governmental protocol for establishing a cryptographic enterprise in Indonesia mandates a tangible establishment and continuous personnel to avert spurious organizations and guarantee proficient hazard administration. This necessity arises from the obligation for expeditious collaboration with state overseers and patrons.
Licenses for Indonesian cryptocurrency necessitate adherence to esoteric criteria for cyber defense, encompassing the establishment of a multi-layered cryptographic system and the execution of periodic scrutiny, to guarantee steadfast safeguarding of individuals' confidential particulars and transactional privacy.
State authorities in Indonesia underscore the imperative for fiscal market facilitators to comply with anti-laundering statutes. Cryptographic licensees are compelled to adopt protocols for client identification, business credibility verification, and fiscal transaction scrutiny to detect and obstruct dubious dealings. Cutting-edge technologies and dedicated fiscal oversight divisions are indispensable for efficacy.
Indonesian officials are authorizing cryptocurrency enterprises, enacting considerable juridical responsibilities such as preserving fiscal chronicles and presenting taxation declarations. This exemplifies their dedication to candid marketplace progression and enticing bona fide contributors for enduring collaboration and statutory adherence.
Cryptocurrency magnates from Indonesia may procure licenses for their ventures; however, the procedure necessitates corroborating the sustainability of the commercial paradigm, fiscal capital, and adherence to statutory requisites. Juridical assistance is paramount for prosperous crypto enterprises, encompassing services such as business schema scrutiny, corporate inscription, treaty mediation, regulatory advisory, and governmental representation. This guarantees an unimpeded progression for both nascent and seasoned crypto undertakings.
Permitted Cryptocurrency Activities for Licensed Companies in Indonesia
According to Indonesian law, crypto-assets are defined as intangible assets expressed in digital form, the functioning of which is based on the use of cryptographic methods, which ensures the regulation of issue, accounting of rights to such assets and transactions with them using distributed registries without a centralized issuer or a single repository of information.
Having received a license to trade crypto assets in Indonesia, you can engage in the following activities:
- services for exchanging fiat currencies for cryptocurrencies and vice versa;
- services for storing clients’ digital assets in special wallets;
- development and release of your own tokens, subject to compliance with all legal requirements;
- services for trading derivatives based on cryptocurrencies.
Procedure for obtaining a crypto license in Indonesia
Indonesia's cryptocurrency enterprise regulatory schema is undergoing vigorous cultivation, eliciting heightened curiosity in licensure protocols, as it aids in fostering a propitious capital infusion milieu.
Bappebti, the overseer, guarantees juridical clarity within the digital asset domain by establishing stringent criteria. This mitigates perils from illicit actions and augments investor trust. A Crypto Service Provider License in Indonesia is obligatory for lawful market operation and adherence to prevailing statutes.
Obtaining permission for crypto activities in Indonesia involves the following steps:
- Company registration in Indonesia on the website of the Ministry of Investments.
- Collection of a complete package of documents.
- Submitting an application with a complete set of documents for licensing.
- Regulator inspection.
- Issuance of a crypto license.
The nascent phase of establishing a cryptocurrency enterprise in Indonesia entails ascertaining the juridical person registration modality, frequently utilizing the PT PMA designation for equity allocation. A comprehensive business stratagem is proffered, substantiating the viability of digital asset flux and guaranteeing the legitimacy of proceedings.
Upon the conclusion of administrative formalities, the licensee composes a dossier of records, encompassing particulars of advantageous proprietors, an exhaustive Statute, subscribed equity and governance framework, scope of operations and objectives, alongside consignments affirming the stipulated minimum subscribed capital.
To procure a digital asset service provider license in Indonesia, postulants must proffer a technical information security schema, encompassing cryptographic protocols, algorithms, Know Your Customer (KYC) tenets, and anti-money laundering (AML) contrivances. Meticulous documentation formalization, including rendition into Indonesian and legal authentication, is paramount.
The dossier for procuring a cryptocurrency charter in Indonesia must be dispatched to an official entity supervising the auxiliary fiscal instruments and digital assets sector. The petition is deliberated after an interval of several months, scrutinizing the submitted records and the repute of the beneficial proprietors. The overseer appraises the petitioner’s openness and the security of undertakings. Should transgressions of extant statutes or discrepancies be uncovered, the petition may be repudiated or reverted to the petitioner for the rectification of the shortcomings.
The overseer appraises the licensee corporation's conformity with informational fortification stipulations, scrutinizing program dependability and protocols to avert illicit entry. They further assess the entity's fiscal steadfastness, emphasizing equity sufficiency and pecuniary assurances.
The governmental institution's accreditation process bestows upon a commercial entity the authorization to function with intangible monetary assets within the national domain. This facilitates ingress to regional settlement frameworks and trading platforms, thereby drawing capital inflows. Preserving licenses for cryptographic endeavors in Indonesia necessitates adherence to statutory stipulations, encompassing periodic documentation and prompt remittance fulfillment.
It is noteworthy that the Indonesian regulator FSA demonstrates an innovative approach to regulation of the crypto market in Indonesia by introducing digital tools such as SPRINT platform. This initiative aims to reduce administrative barriers for crypto industry entities, while providing a high level of legal certainty and strengthening confidence in the national financial system.
The introduction of SPRINT software marked the beginning of a new era in the development of Indonesian cryptocurrency and fintech initiatives. Streamlining internal processes, improving communication channels and providing access to a regulated sandbox help create the conditions for the formation of a dynamic and inclusive financial environment that meets modern challenges.
Cost and deadline for obtaining a crypto license in Indonesia
The terminus for procuring a crypto charter in Indonesia may extend to half a year, encompassing civil registry and supervisory scrutiny. Elements influencing this period comprise the intricacy of the organizational composition, the count of originators, the magnitude of envisaged enterprise, and the efficacy of public institutions conferring licenses.
It is necessary to emphasize that the insufficiency of submitted documents, expressed in their incorrect execution, incompleteness or content of false information, can significantly prolong the procedure for considering an application for crypto licensing in Indonesia. In such situations, the supervisory authority, as a rule, initiates the return of documents to the applicant for revision, which entails additional time and financial costs. In addition, one should be prepared for potential delays due to regulatory developments, especially in the context of the transfer of some powers to FSA.
Cryptocurrency business licensing in Indonesia may be accompanied by significantly higher financial costs, given that it involves the need for an integrated approach, including the integration of payment interfaces, the implementation and adaptation of AML/KYC procedures, and staff training activities with an emphasis on regulatory requirements in the field of digital assets.
Let's focus your attention! The forthcoming epoch is anticipated to witness heightened jurisprudential governance, concentrating on oversight apparatus and pioneering advancements. The FSA's ancillary edicts may profoundly influence the statutory framework, necessitating market stakeholders to acclimate and assimilate novelties for strategic preponderance.
Are cryptocurrencies subject to tax in Indonesia?
Having made a decision to obtain a license to operate cryptocurrency in IndonesiaPlease note that the tax system classifies cryptocurrencies as goods subject to both Value Added Tax (VAT) and Personal Income Tax (PIT). According to current legislation, all transactions with cryptocurrencies, including purchases, sales and exchanges, are subject to tax.
To ensure the effective collection of taxes on transactions with cryptocurrencies, Indonesian legislation assigns the function of tax agents to cryptocurrency exchanges. Exchanges are required to withhold VAT and PPh for each transaction and transfer them to the budget. Thus, the taxpayer effectively pays taxes upfront when completing the transaction. An important aspect of taxation of cryptocurrencies in Indonesia is the obligation of taxpayers to declare their income from transactions with digital assets. Failure to fulfill this obligation or provision of false information entails administrative and/or criminal liability.
Meanwhile, the sharp increase in crypto transaction volumes has led to a significant increase in tax contributions to the Indonesian budget, reaching an amount of 942.88 billion rupiah by October 2024. This fact confirms the effectiveness of government policy aimed at the legalization and inclusion of digital currencies in the regulated financial sector.
Conclusion
Indonesia, a vanguard in digitization and fiscal expansion, proffers external stakeholders the opportunity to diversify their capital holdings and tap into the burgeoning cryptographic currency sector within the Asiatic expanse.
A cryptocurrency charter in Indonesia confers upon a juridical person complete market engagement, facilitating formal collaborations with monetary institutions, brokerage houses, and payment platforms, streamlining external capital infusion and ingress to fiscal assets.
The Indonesian cryptocurrency sector contends with fierce rivalry from multinational conglomerates and indigenous establishments. To acquire an accreditation, enterprises must possess a distinctive value proposition, a steadfast stance, and avant-garde remedies, as fiscal precariousness can curtail their potentialities.
To attenuate juridical perils in acquiring a permit and effectuating licensed undertakings, it is advisable to enlist adept attorneys. Our establishment offers holistic assistance in procuring a cryptocurrency charter in Indonesia, encompassing dossier formulation, liaison blueprint, and patron advocacy throughout the licensure procedure.






 A complete guide to starting a tourism business in Indonesia
A complete guide to starting a tourism business in Indonesia  Real estate in Bali: buying property
Real estate in Bali: buying property  Buying property in Indonesia
Buying property in Indonesia  Start an IT Company in Indonesia
Start an IT Company in Indonesia  Crowdfunding in Indonesia
Crowdfunding in Indonesia 



